本篇笔记概述了数字系统和信息的基本概念,包括数字电路、数字信号与模拟信号的区别,逻辑系统的分类(组合电路与时序电路),以及数字计算机和嵌入式系统的结构与设计过程。此外,还介绍了数字系统中的进制、编码方式(如 BCD 码、格雷码和奇偶校验码)等内容,帮助读者理解数字逻辑设计的基础知识。(由 gpt-4o-mini 生成摘要)
Word Table
1. 数字系统 Digital Systems
1.1. 信息表达 Information Representation
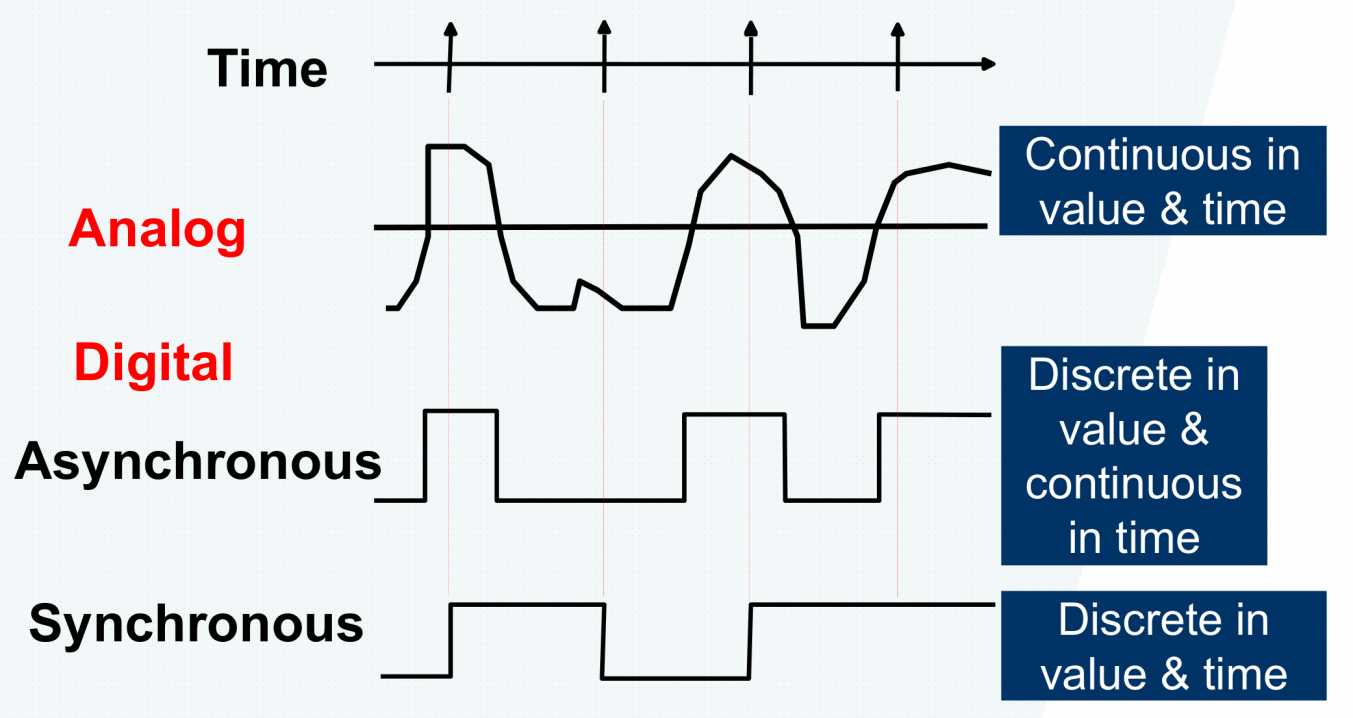
- 模拟信号(analog signal):取值是连续(continous) 的。
- 数字信号(digital signal):取值是离散(discrete) 的。
- 异步(asynchronous):在变化的时间点上是连续的。
- 同步(synchronous):在变化的时间点上也是离散的;由时钟脉冲控制。
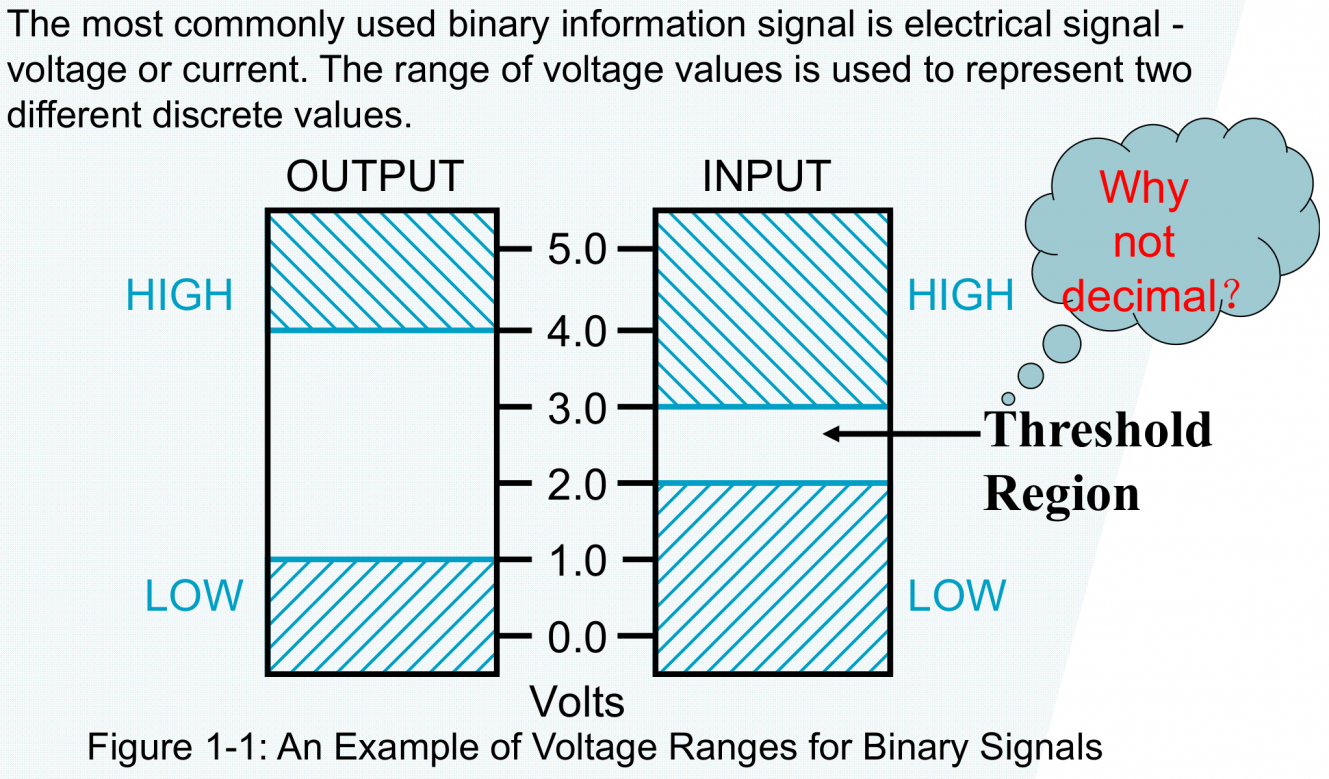
- HIGH 和 LOW 是噪声容限。
- 图中 HIGH 和 LOW 的接受范围内存在一段阈值区间,落在这一部分的电平是未定义(undefined) 的,也被称为是浮动(floating) 的。如果输出的电平是在浮动区间的,那么其认定值将是随机的。
- 硬件层面上,将模拟信号转化为数字信号的工作一般通过晶体管(transistors) 实现。
输出时的接受范围会比输入时的略小一些。其目的是为了进一步提高电路在噪音等异常影响下也能正常表现的能力。 “宽进严出”规则
事实上,在信息的对应上,虽然将高低电平同 HIGH/LOW 联系是很自然的,但是将他们同 true/false 或者 1/0 联系其实并不唯一。但是在一般情况下(我们称之为 positive logic),我们都认为 HIGH ~ true ~ 1, LOW ~ false ~ 0。 Positive Logic
1.2. 逻辑系统 Logic System
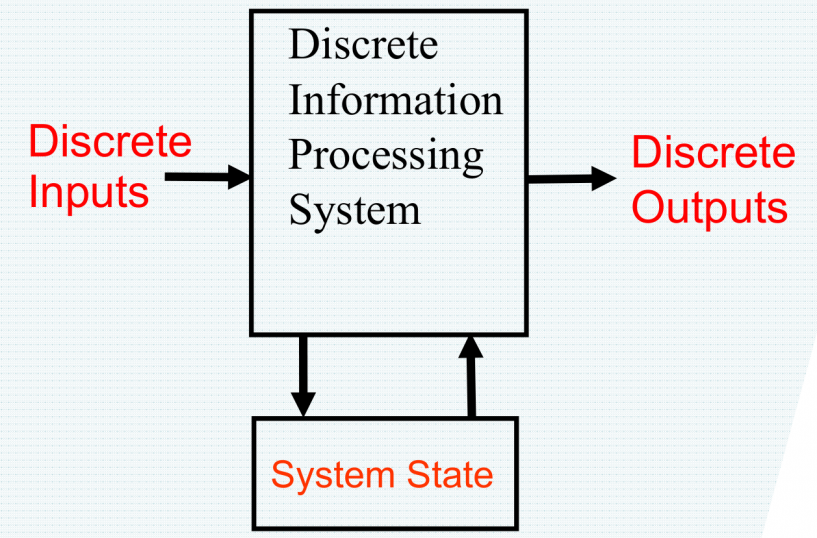
- 组合电路和时序电路的主要区别在于有没有系统状态(system state)。
1.2.1. 组合电路 Combinational Logic System
- 没有状态 No state present
- 只需要推导出一个函数即可 Output Function: Output = Function(Input)
1.2.2. 时序电路 Sequential Logic System
- 存在状态 State present
- Synchronous Sequential System <=> State updated at discrete times
- Asynchronous Sequential System <=> State updated at any time
- 次态方程 State Equation: Next State = Function(Current State, Input)
- 输出方程 Output Function: Output = Function(State, Input(optional))
1.3. 数字计算机 Digital Computer
数字计算机(digital computer):A general-purpose system used to process the discrete values
嵌入式系统(embedded system):Computers as integral parts of other products
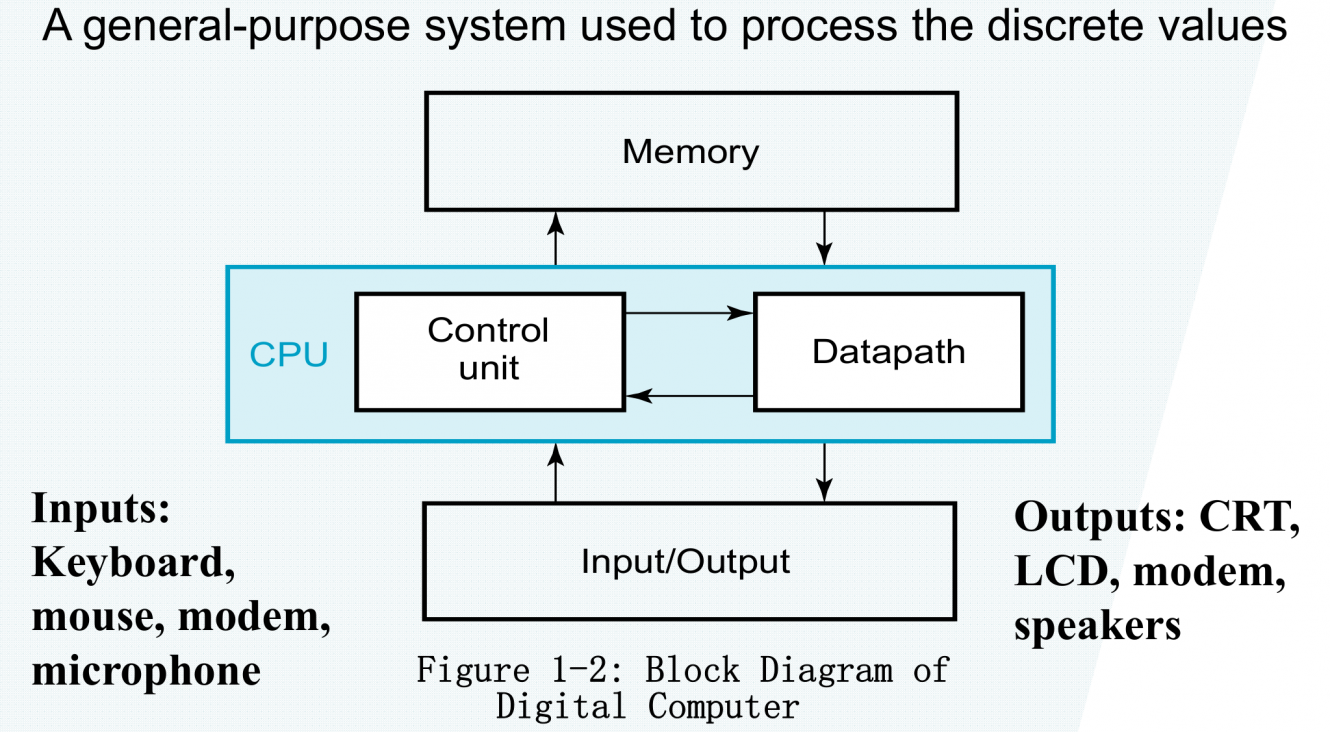
- 是典型的 Synchronous Sequential System。
1.3.1. 计算机系统结构
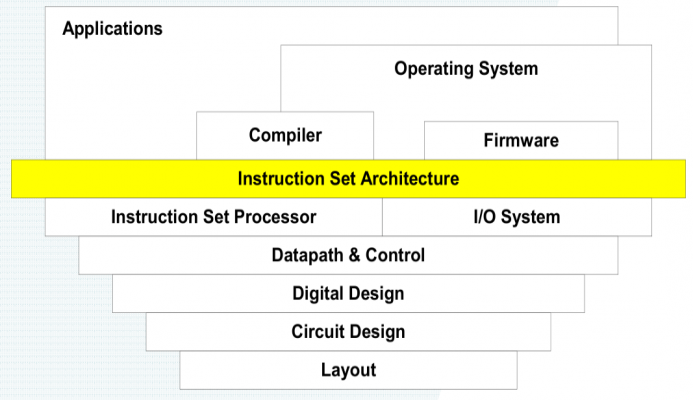
- Algorithm
- Programming Language
- Operation System
- 指令集结构 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
- Microarchitecture
- Register Transfer
- Logic Circuit
- Transistor Circuit
1.3.2. 设计过程 Design Procedure
如何设计一个程序?
- Specification
- Formulation
- Optimization
- Apply 2-level and multiple-level optimization
- Draw a logic diagram or provide a netlist for the resulting circuit using ANDs, ORs, and inverters
- Technology Mapping
- 用已有的原件实现功能(eg. 实现 XOR Gate
- Verification
- 验证结果是否正确
2. 数字系统 Number System
2.1. 进制 Base
| Decimal | Binary | Octal | Hexadecimal |
|---|---|---|---|
| base 10 | base 2 | base 8 | base 16 |
- 进制(radix/base):collection of numberal symbols used to represent numbers in number system
- 权重(digit weight): the counting unit value of basic digital symbols in different position. ie, weight W
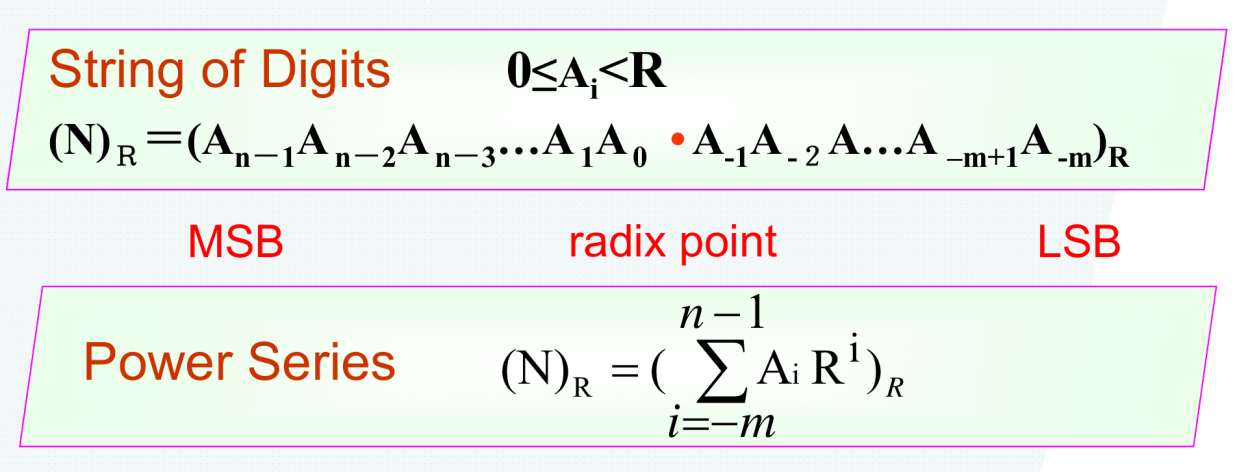
- 表示(representation):digits of a number N are listed From left to right, length n+m(有整数部分和小数部分)
- String of Digits:
- 全展开式(Power Series):
2.2. 进制转换
略。
- 别忘了小数怎么搞。
- 舍入(rounding) 的问题。
3. 编码 Coding
3.1. 独冷码 & 独热码 One-Hot & One-Cold Code
独热码(one-hot) 要求比特向量中只有一位是 1,例如 0001,0010,0100,1000 等;对应的还有独冷码(one-cold)。
使用这种编码的好处是,决定或改变状态机目前的状态的成本相对较低,容易设计也容易检测非法行为等。
但是相对应的,缺点是信息表示率较低,非法状态非常多而有效状态很少。
3.2. BCD 码 Binary Coded Decimal Code
3.2.1. 8421 Code
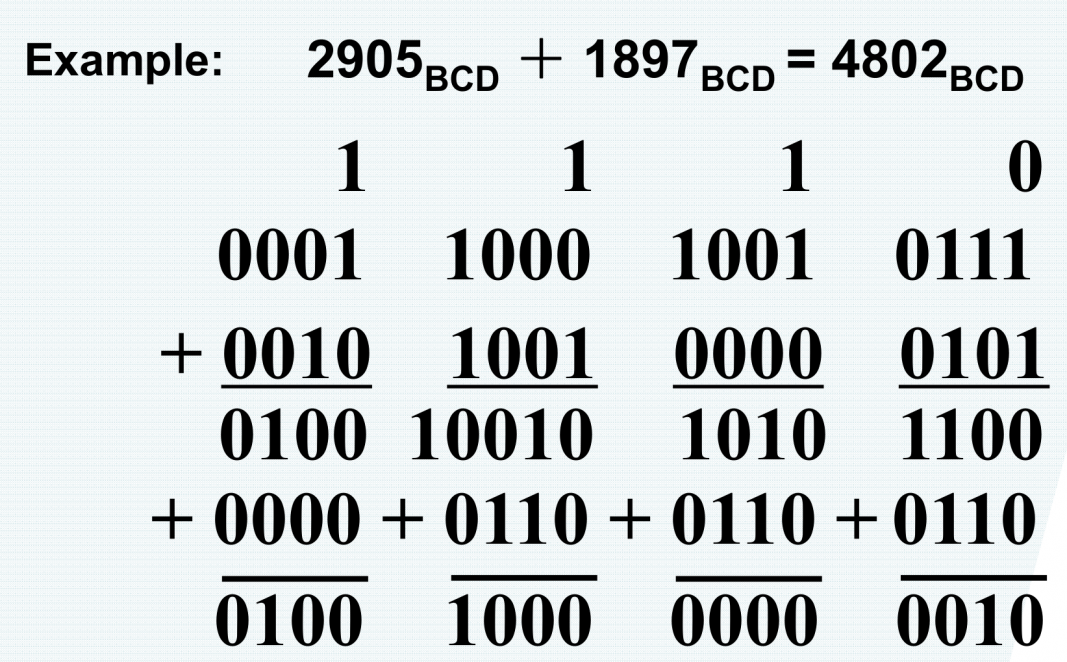
最经典的 BCD 码是 8421 码,用 4 位二进制表示一个十进制位,weight 分别为 8421,所以 BCD 码也叫做 8421 码。
- BCD 码在做加法时,类比十进制加法一样按 4 位一组计算。
- 当两位相加的结果大于 10 时需要做一个 +6 的修正。
3.2.2. Excess3 Code
余三码(Excess3) 是 BCD 码的一个改进,其核心思路是在 BCD 码的基础上,增加一个大小为 3 的偏移量。(每一位都是先 +3 再转化成二进制)
- 进位检测:注意到 ,这样十进制下能进位的两个数位,在余三码下也刚好能进位。
3.2.3. 2421 Code
2421 码与 8421 码类似,但是每一位的权值分别为 2421。 中的每一个数都对应一个唯一的 2421 码,但将不在这一对应表中的二进制编码转换回十进制时也能对应到 中的数字。
- 2421 码的一个特性是 和 的 2421 码互补,其中 时的 2421 码就是其二进制,而 的 2421 码就是 与 异或后的结果。
3.3. 格雷码 Gray Code
格雷码(gray code) 是一种可靠性编码(reliable code)。相邻的两个数字的格雷码只有一个 bit 上的 0/1 不同。
Reliable codes are codes that can reduce error, detect error and correct error are called reliable code. 可靠性编码
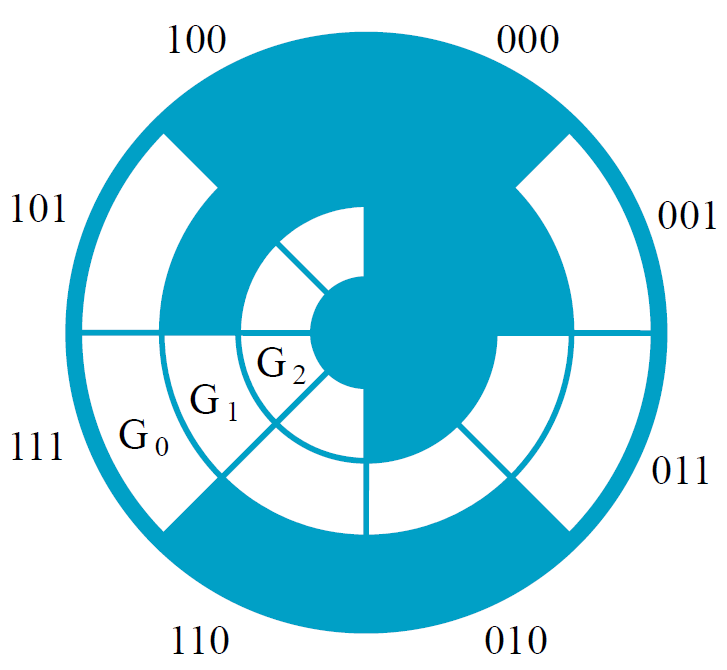 从光学透镜的角度理解格雷码
从光学透镜的角度理解格雷码
数字 对应的格雷码为:
二进制反射格雷码(Binary Reflected Gray Code, BRGC)
3.4. 奇偶校验码 Parity Code
奇偶校验码(parity code) 也是一种可靠性编码,分为偶校验码和奇校验码两种。偶校验码(even parity code) 保证数据中为 1 的 bit 数为偶数,奇校验码(odd parity code) 保证为奇数。
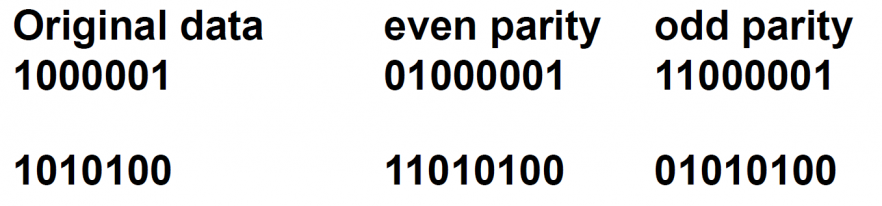 奇偶校验码示例
奇偶校验码示例
- 需要注意是奇校验还是偶校验
- 需要注意是补在最高位还是最低位